
Master of Science [M.Sc] (Genetics and Plant Breeding) From Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh
| Years | year 1 | year 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Year Wise fees | ₹39,140 | ₹39,140 | ||
| Semester | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Total Fees | ₹19570 | ₹19570 | ₹19570 | ₹19570 |
| Tuition fees | ₹19570 | ₹19570 | ₹19570 | ₹19570 |
Junagadh Agricultural University Master of Science [M.Sc] (Genetics and Plant Breeding) Ranking

Do you think the Rankings are wrong ? Report Here
Course Description
Master of Science in Genetics and Plant Breeding Top Colleges, Syllabus, Scope and Salary
M.Sc. in Genetics and Plant breeding is a 2-year postgraduate course, sub-divided into 4 semesters, of 6 months each. The course is an advanced study of:
- Methods of improvement of crops and plants by inserting desirable traits to them
- application of genetics in conserving the environment while addressing the growing need for food security.
The basic qualification required for pursuance of the course is B.Sc. in a relevant discipline, completed from a recognized university. In India, the average annual fee charged for the course ranges between INR 2 and 6 lacs, varying across institutes.
| Master of Science in Uttar Pradesh | Master of Science in Rajasthan | Master of Science in Kerala | Master of Science in Bihar |
Admission to the course is offered based on the candidate’s performance in a relevant entrance test, followed by a round of counseling.
The course’s curriculum integrates theoretical and practical components of the study.
Successful postgraduates of the course are hired in fields such as:
- Plant Breeding Centers
- Agriculture Sector
- Nurseries
- Agriculture Ministry
- Crop Plantation Facilities
- Colleges & universities, and such others.
The average initial annual salary offered to such postgraduates ranges between INR 3 and 10 Lacs, increasing with the candidate’s experience and expertise in the field.
M.Sc. in Genetics & Plant Breeding: Course Highlights
Tabulated below are the major highlights of the course.
| Course Level | Postgraduate |
| Duration | 2 Years |
| Basic Eligibility | Graduation (B.Sc.) completed from a recognized university. |
| Admission Process | Merit-based/ Based on counseling after qualification of entrance exam. |
| Examination Type | Semester System |
| Major Entrance Exams | IIT JAM, NIPER JEE, PGIMER Chandigarh, DAVV, Admission Non-CET, Calcutta University M. Sc. Admission, NIT Admission Test, etc. |
| Total Course Fee | INR 2 to 6 Lacs |
| Top Recruiting Fields/ Areas | Colleges & universities, agriculture sector, nurseries, plant breeding centers, plantation crop plants, agriculture ministries, research laboratories, crop research directorates, etc. |
| Job Positions | Plant Breeder, Agronomist, Corn Breeder, Cotton Agronomist, Research Associate, Senior Research Fellow, Launch and Support Specialist, Application Support Specialist, Programmer Analyst, Conversion Centre Manager, and such. |
| Average Initial Salary | INR 3 to 10 Lacs |
M.Sc. in Genetics and Plant Breeding: What is it About?
Genetics and Plant Breeding is a new and flourishing branch of Modern Biology, which is:
-
the application of Molecular Biology to insert desirable traits into plants.
- selecting the best-quality plants in any given field, growing them to full seed and then using that seed to grow further generations
- the scientific mechanism of transforming the genetic composition of plants over time, for biological and commercial purposes.
Successful postgraduates of the course interested in pursuing further studies in the discipline may pursue Ph.D., M. Phil., or higher research in the subject.
- Genetics and Plant Breeding is primarily about:
- the various technologies and ways to improve varieties and genetic stocks.
- transforming the genetic make-up of plants for better grain quality, yielding ability, and resistance to insect pests and diseases.
- maintaining and evaluating the diversity of genetic stock.
- innovative scientific ways of developing special uses for a variety of species, such as soybean with improved seed composition for food use, corn with high and low protein or oil contents, etc.
- producing improved cultivars and novel germplasms
- creating innovative breeding technologies for positively impacting the production of food, feed, and fiber.
Top Institutes offering M.Sc. in Genetics and Plant Breeding
Mentioned below are the names of some of the top institutes and colleges in the country offering a Master’s degree in Genetics & Plant Breeding, along with their corresponding locations and average annual fees charged by each.
Eligibility for M.Sc. in Genetics and Plant Breeding
In order to pursue the course, interested eligible candidates are required to satisfy the following minimum eligibility criteria.
-
completed from a recognized institute.
- A minimum aggregate score of 50% (45% for SC/ST/OBC candidates) at the level of graduation.
- Graduation needs to have been completed in any of:
- Agriculture
- Horticulture
- Forestry
- Biology
- Candidates awaiting their graduation examination’s results are also eligible to apply on provisional basis.
- Preferably, a minimum of 12 months of professional experience, as most reputed institutes prefer candidates with work experience.
| Master of Science in Madhya Pradesh | Master of Science in Maharashtra | Master of Science in Tamil Nadu | Master of Science in West Bengal |
M.Sc. in Genetics and Plant Breeding: Admission Process
Most institutes in India offering the course admit students based on their performance in a relevant entrance test. Some institutes also admit students based on the candidate’s obtained merit at the level of graduation, while some conduct their own entrance tests for offering admission. Admission process generally varies across colleges.
Some such major entrance exams conducted in the country for admission to the course are as follows.
- IIT JAM (Joint Admission Test)
- NIPER JEE (Joint Entrance Exam)
- PGIMER Chandigarh
- DAVV Admission Non-CET
- Calcutta University M. Sc. Admission
- MJP Rohilkhand University Entrance Test
- Central University of Gujarat Admission Test
- DU (Delhi University) PG Admission Test
- BIT MESRA Integrated Admission Test
- BVP M. Sc. Entrance Exam
- NIT Karnataka Admission Test
M.Sc. in Genetics and Plant Breeding: Syllabus and Course Description
A semester-wise breakup of the course’s syllabus is tabulated below.
Semester I |
Semester II |
| Mendelian Genetics | Molecular Genetics |
| Techniques in Cell Biology | Cytogenetics |
| Cytology | Plant Breeding |
| Elective 1 | Plant Biochemistry |
| - | Elective 2 |
Semester III |
Semester IV |
| Genetic Engineering | Population Genetics |
| Plant Biotechnology | Development Genetics |
| Environmental Genetics | Biosystematics |
| Modern Methods in Crop Genetics | Elective 4 |
| Elective 3 | - |
| Elective 1 | Elective 2 |
| Biophysics | Plant Tissue Culture |
| Applied Palynology | Transgenic Plants |
| Elective 3 | Elective 4 |
| Biotechnology | Plant Cell Culture Technology |
| Biosystematics | Phytochemicals |
M.Sc. in Genetics and Plant Breeding: Career Prospects
Genetics and Plant Breeding is an emerging field and a lucrative career option, as it plays an important role in the progress of a nation, by contributing to elimination of starvation and improvement of food quality, by means of genetic modification.
Qualified Genetics and Plant Breeding professionals can find lucrative employment across both private and government sectors, in areas such as:
- Colleges and universities
- Agriculture Sector
- Nurseries, Plant Breeding Centers
- Plantation Crop Plants
- Agriculture Ministry
- Research Laboratories, Crop Research Directorates, and such.
Successful postgraduates of the course interested in pursuing further studies in the discipline may go for Ph. D. M. Phil., or further research in the subject.
Tabulated below are some of the popular professional avenues open to such postgraduates, along with the corresponding salaries and basic job responsibilities associated with each one of them.
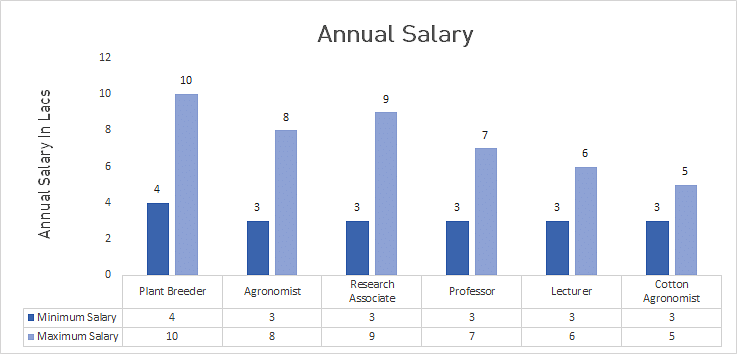
| JOB PROFILE | JOB DESCRIPTION | AVERAGE ANNUAL SALARY |
| Plant Breeder | Plant Breeders are responsible for improving existing plant species, creating new ones in order to improve appearance, resistance to disease, yield and other characteristics. Also, they keep records of research and findings. They may work in an academic, commercial, or research setting. | INR 4 to 10 Lacs |
| Agronomist | Agronomists professionally experiment with plantation modes and plan studies to improve crop yields. They study a farm's crop production to discern the best ways to plant, harvest, and cultivate plants, regardless of the climate. | INR 3 to 8 Lacs |
| Research Associate | Research Associates are responsible for monitoring the progress of research projects and for coordinating information between departmental sections. They perform highly specialized and advanced experiments, and collect, prepare, analyze, and evaluate specimens and/or tissue cultures. Additionally, they perform a wide and complex variety of test, assays, and studies. | INR 3.5 to 9 Lacs |
| Professor | Professors’ responsibilities are divided between teaching, researching, and keeping up with current research activities in their areas of expertise. They may have one or more areas of expertise. | INR 3 to 7 Lacs |
| Lecturer | Lecturers are employed by universities and higher education establishments to undertake teaching and other administrative duties within a specialist subject area. They also encourage personal development via tutorial or pastoral work, invigilate examinations, etc. | INR 3 to 6 Lacs |
| Cotton Agronomist | Cotton Agronomists professionally contribute to the development of the research methodologies and strategies, and estimate areas with cotton-growing potential by collecting data, and working on improvement of cotton varieties and production. | INR 3 to 5 Lacs |
Eligibility Criteria
A candidate for admission to the Master degree programmes should have minimum 60% marks (55% marks for SEBC/ST/SC ) OR 6.00 OGPA (Out of 10) at the bachelor degree level from a recognized university.
Admission Guidelines
- The eligible applicant must appear in entrance test.
- The basis of selection of candidate for the admission shall be the merit.
- The merit list shall be prepared by giving 50:50 weightage to the marks of OGPA (percentage marks) of the last degree and common entrance test examination.
Course Details
Fee for Girls:
Fee: 12570- Per Semester.
Course Finder
Search from 20K+ Courses and 35+ Streams
Popular Streams:
Junagadh Agricultural University Latest News
Junagadh Agricultural University Result 2022: Entrance Exam, Merit List


Discover More Colleges
![Anand Agricultural University - [AAU]](https://images.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/appImage/25477_AAU.jpg?tr=h-111.44,w-263,c-force)

![Sardarkrushinagar Dantiwada Agricultural University - [SDAU]](https://images.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/appImage/25510_SDAUNIVERSITY_APP.jpg?tr=h-111.44,w-263,c-force)






















![National Bureau of Fish Genetic Resources - [NBFGR]](https://images.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/col6676.jpg?tr=h-72,w-72,c-force)
![Sardarkrushinagar Dantiwada Agricultural University - [SDAU]](https://images.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1440134531jpjpjpjp.jpg?tr=h-72,w-72,c-force)
![Jawaharlal Nehru Krishi Vishwa Vidyalaya - [JNKVV]](https://images.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1489052046JNKVVImage.jpg?tr=h-72,w-72,c-force)
![Amity Institute of Organic Agriculture - [AIOA]](https://images.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/col6516.jpg?tr=h-72,w-72,c-force)
![National Research Centre for Orchids - [ICAR]](https://images.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1422251501logogff.jpg?tr=h-72,w-72,c-force)
![National Research Centre on Yak - [NRCY]](https://images.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/col6699.jpg?tr=h-72,w-72,c-force)
![Anand Agricultural University - [AAU]](https://images.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1394535486untitled.JPG?tr=h-72,w-72,c-force)

![Central Institute for Subtropical Horticulture - [CISH]](https://images.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/col6534.jpg?tr=h-72,w-72,c-force)




Comments